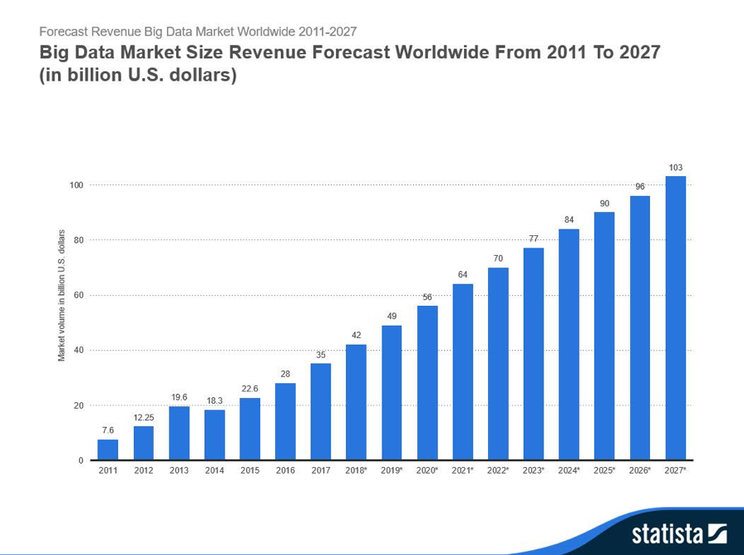
In 2018, China’s authorities are ready to invest $ 14 bn in digital economy over the next five years.
To finance the initiative, the State Committee for Development and Reform signed a cooperation agreement with the Bank of China, reports TASS. The agreements were concluded during the work of the Digital Economy and Digital “One Belt, One Way” conference, which is now taking place in the capital of eastern Zhejiang province, Hangzhou.
The funds will be spent on the development of such areas as online delivery, smart cities, cloud services, projects related to the processing of a large data array (Big data) and “digital Silk Road”. The conference noted that the development of high technologies and the economy of the modern type is included in the list of priorities in terms of China's economic development.
To finance the initiative, the State Committee for Development and Reform signed a cooperation agreement with the Bank of China, reports TASS. The agreements were concluded during the work of the Digital Economy and Digital “One Belt, One Way” conference, which is now taking place in the capital of eastern Zhejiang province, Hangzhou.
The funds will be spent on the development of such areas as online delivery, smart cities, cloud services, projects related to the processing of a large data array (Big data) and “digital Silk Road”. The conference noted that the development of high technologies and the economy of the modern type is included in the list of priorities in terms of China's economic development.
From the graph we can see that big data market size is increasing every year and China is now one of the countries in which the big data market will reach $ 5.5 b in 2018.
Medicine as national priority
Promoting the use of big data in medicine is a national priority in China. In June 2016, the State Council of China issued an official notice on the development, and use of big data in the healthcare sector. The council acknowledged that big data in health and medicine were a strategic national resource and their development could improve healthcare in China, and it set out programmatic development goals, key tasks, and an organisational framework.
After regional health data centres were established in Shanghai and Ningbo, the National Health and Family Planning Commission announced in 2016 that China would establish more regional and national centres and industrial parks that focused on big data in health and medicine as part of a national pilot programme to make more meaningful use of these data.
China's healthcare industry is leveling up particularly in the use of big data technology for medicine, and a newly established organization aims to improve big data application in the health and biotech sectors.
Where do healthcare data come from?
Example of sources of medical big data are administrative and claims data, routine population statistics and major disease surveillance data, real world data, such as electronic medical records, medical imaging, and data from health examinations. Also research data, including biomarkers, and multi-omic information from clinical trials or cohort studies and registries (eg, of devices, procedures, and diseases), data from mobile medical devices or reported by patients.
CECD and Wuxi AppTec, an example
China Electronics Data Service Co., Ltd. ("CECD") and WuXi AppTec announced in November 2018 to set up a joint venture, CW Data, to offer one-stop big data solutions for the healthcare sector. Based on hospital medical and prescription data, CW Data will provide healthcare data solutions for pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology companies, payers, providers, policy makers, healthcare professionals and other life science industry organizations, thereby further promoting the innovation and development of the China's healthcare ecosystem and benefiting more Chinese patients.
Dr. Hakon Gudbjartsson, PhD and WuXi NextCODE CIO, knows what it takes to be a data visionary.
Using sequence data, he and his team are enabling organizations to unlock the power of the genome to enhance health and wellness.
WuXi NextCODE is a genomic information company and global platform for genomic big data. Over the past 20 years, they’ve amassed the world’s largest database of human genome sequences. If you pare your DNA, you would find about 5 million differences.
“The challenge is to take a dataset of 5 million and figure out the differences or mutations that are important — which ones are the causes of rare diseases, which ones are the causes of cancer, and how to treat patients,” Dr. Gudbjartsson explained.
At the heart of the WuXi NextCODE platform is the genomic relational database, the only data architecture designed to optimize the use of massive genomic data.
By leveraging NetApp Cloud Data Services, the genome platform makes it possible to integrate data on the fly to deliver unprecedented computational efficiency.
Today, this architecture underpins preeminent genomics efforts on four continents and is the emerging global standard for organizing, mining, and sharing large-sequence datasets.
Sofiya Sergeeva
Medicine as national priority
Promoting the use of big data in medicine is a national priority in China. In June 2016, the State Council of China issued an official notice on the development, and use of big data in the healthcare sector. The council acknowledged that big data in health and medicine were a strategic national resource and their development could improve healthcare in China, and it set out programmatic development goals, key tasks, and an organisational framework.
After regional health data centres were established in Shanghai and Ningbo, the National Health and Family Planning Commission announced in 2016 that China would establish more regional and national centres and industrial parks that focused on big data in health and medicine as part of a national pilot programme to make more meaningful use of these data.
China's healthcare industry is leveling up particularly in the use of big data technology for medicine, and a newly established organization aims to improve big data application in the health and biotech sectors.
Where do healthcare data come from?
Example of sources of medical big data are administrative and claims data, routine population statistics and major disease surveillance data, real world data, such as electronic medical records, medical imaging, and data from health examinations. Also research data, including biomarkers, and multi-omic information from clinical trials or cohort studies and registries (eg, of devices, procedures, and diseases), data from mobile medical devices or reported by patients.
CECD and Wuxi AppTec, an example
China Electronics Data Service Co., Ltd. ("CECD") and WuXi AppTec announced in November 2018 to set up a joint venture, CW Data, to offer one-stop big data solutions for the healthcare sector. Based on hospital medical and prescription data, CW Data will provide healthcare data solutions for pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology companies, payers, providers, policy makers, healthcare professionals and other life science industry organizations, thereby further promoting the innovation and development of the China's healthcare ecosystem and benefiting more Chinese patients.
Dr. Hakon Gudbjartsson, PhD and WuXi NextCODE CIO, knows what it takes to be a data visionary.
Using sequence data, he and his team are enabling organizations to unlock the power of the genome to enhance health and wellness.
WuXi NextCODE is a genomic information company and global platform for genomic big data. Over the past 20 years, they’ve amassed the world’s largest database of human genome sequences. If you pare your DNA, you would find about 5 million differences.
“The challenge is to take a dataset of 5 million and figure out the differences or mutations that are important — which ones are the causes of rare diseases, which ones are the causes of cancer, and how to treat patients,” Dr. Gudbjartsson explained.
At the heart of the WuXi NextCODE platform is the genomic relational database, the only data architecture designed to optimize the use of massive genomic data.
By leveraging NetApp Cloud Data Services, the genome platform makes it possible to integrate data on the fly to deliver unprecedented computational efficiency.
Today, this architecture underpins preeminent genomics efforts on four continents and is the emerging global standard for organizing, mining, and sharing large-sequence datasets.
Sofiya Sergeeva