Recent performance
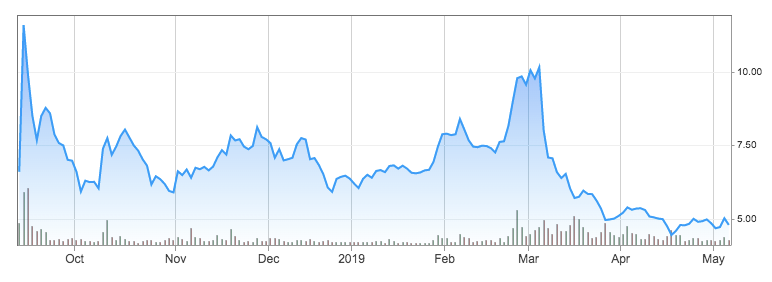
NIO ((NYSE:NIO) is a Chinese startup company founded in 2014 which operates in the premium electric vehicle (EV) sector. Being a new company, the has only two models in its product portfolio: the ES8 and the ES6. The firm has started delivering the ES8 in June 2018 and will begin delivering the ES6 in June 2019. The company’s mission is highlighted in its Chinese name, Weilai, which means Blue Sky Coming and highlights the company’s commitment to a more environmentally friendly future. NIO wants to achieve this by driving innovations in the fields of connectivity, autonomous driving and artificial intelligence, leveraging on a strong brand and high customer satisfaction. On the 12th September 2018, NIO got listed on the NYSE at a share price of $6.25, with a valuation of $6.68 billion. Since then, the company has witnessed severe fluctuations in its stock price, making NIO’s stock a quite volatile investment. Such volatility is highlighted by the stock performance in the recent months. Since the 3rd of March, the stock price has fallen by almost 50%, falling from $10.16 per share to a value of about $4.88 per share (7th May).
NIO ((NYSE:NIO) is a Chinese startup company founded in 2014 which operates in the premium electric vehicle (EV) sector. Being a new company, the has only two models in its product portfolio: the ES8 and the ES6. The firm has started delivering the ES8 in June 2018 and will begin delivering the ES6 in June 2019. The company’s mission is highlighted in its Chinese name, Weilai, which means Blue Sky Coming and highlights the company’s commitment to a more environmentally friendly future. NIO wants to achieve this by driving innovations in the fields of connectivity, autonomous driving and artificial intelligence, leveraging on a strong brand and high customer satisfaction. On the 12th September 2018, NIO got listed on the NYSE at a share price of $6.25, with a valuation of $6.68 billion. Since then, the company has witnessed severe fluctuations in its stock price, making NIO’s stock a quite volatile investment. Such volatility is highlighted by the stock performance in the recent months. Since the 3rd of March, the stock price has fallen by almost 50%, falling from $10.16 per share to a value of about $4.88 per share (7th May).
Reasons behind stock price downfall
The reasons behind this sharp fall in price reflect negative investor sentiment following publication of quarterly results on March the 6th. NIO reported a quarterly loss of $509.5 million or 49 cents per share, whereas analysts estimates averaged at 32 cents per share. Much of its was due to a severe decline in deliveries of its ES8 model in January and February, with 1,805 and 811 deliveries respectively in the two months as opposed to 3,318 deliveries in December 2018. As investors expected ES8 deliveries to increase as NIO ramped up its production to meet growing demand for orders, this decline in deliveries clearly revised their expectations downward. To the eyes of investors, declining deliveries are a symptom that perhaps NIO isn’t attracting as much customers as forecasted. In the quarterly report, the company strongly opposes this view by saying that decline in deliveries was due to customers anticipating delivery at the end of 2018 in expectation of subsidy reductions in China in 2019. This theory certainly holds as the Chinese government had warned consumers of its plans to scale back subsidies in the next years and eliminate them totally after 2020. This was confirmed officially on the 26th March, where the government officially announced that it would reduce incentives in the purchase of electric vehicles by 67%, contrarily to market expectations of about 40 to 50 percent.
Yet, the fact that 3,318 represented an optimistic figure for deliveries has still downgraded analyst expectations, since 3,318 was instead before regarded as a lower benchmark of future deliveries of the ES8.
The reasons behind this sharp fall in price reflect negative investor sentiment following publication of quarterly results on March the 6th. NIO reported a quarterly loss of $509.5 million or 49 cents per share, whereas analysts estimates averaged at 32 cents per share. Much of its was due to a severe decline in deliveries of its ES8 model in January and February, with 1,805 and 811 deliveries respectively in the two months as opposed to 3,318 deliveries in December 2018. As investors expected ES8 deliveries to increase as NIO ramped up its production to meet growing demand for orders, this decline in deliveries clearly revised their expectations downward. To the eyes of investors, declining deliveries are a symptom that perhaps NIO isn’t attracting as much customers as forecasted. In the quarterly report, the company strongly opposes this view by saying that decline in deliveries was due to customers anticipating delivery at the end of 2018 in expectation of subsidy reductions in China in 2019. This theory certainly holds as the Chinese government had warned consumers of its plans to scale back subsidies in the next years and eliminate them totally after 2020. This was confirmed officially on the 26th March, where the government officially announced that it would reduce incentives in the purchase of electric vehicles by 67%, contrarily to market expectations of about 40 to 50 percent.
Yet, the fact that 3,318 represented an optimistic figure for deliveries has still downgraded analyst expectations, since 3,318 was instead before regarded as a lower benchmark of future deliveries of the ES8.
Another factor that caused NIO’s stock price to plummet was the above-mentioned cut in government subsidies towards the consumption of electric vehicles. This had repercussions on the industry as a whole, with other Chinese firms operating in the electric vehicle sector such as BYD Co. and BAIC BluePark New Energy Technology Co. losing respectively 3.5% and 4.2% on the market the day of the announcement. However, the company believes that the cut in subsidies will not cause its revenues to fall. Primarily, this is due to the fact that NIO does not intend to cut its prices following the subsidy decrease, meaning consumers will absorb the increase in prices and NIO will not decrease its margins. According to NIO, this is possible due to a decrease in the VAT tax rate for manufacturing industries from 16% to 13%, which the Chinese government announced on the March 5th. The decrease in taxes will reduce prices for consumers and offset the decrease in subsidies. This is especially true for companies like NIO, that operate in the premium segment of the EV market and allow customers to benefit more from the tax decrease due to the higher price of their vehicles. However, some analyst are skeptic on NIO not decreasing its prices. One of these is Robin Zhu, analyst at Bernstein, which says that the decrease in subsidies makes NIO the “most vulnerable” amongst electric vehicle companies in China.
The last important factor that caused market pessimism around NIO was the company’s decision to terminate the plan of building a manufacturing plant in Shanghai. On the contrary, NIO has entered into an agreement with JAC to jointly manufacture cars in JAC’s plant in Hebei. The plant with JAC is expected to remain in force for the next 2-3 years and is expected, after upgrades, to have an annual capacity of 150,000 units. In the long-run, NIO announced it will still focus on joint manufacturing and could potentially enter into agreements with other manufacturers as well. This decision has caused investors to submit a class action, alleging the company misled investors on its intentions regarding the Shanghai plant at the time of its IPO. According to them, the company’s SEC statements almost guaranteed that the plant was going to be constructed. The fact it didn’t is perceived by investors as a fraud since it significantly changes their expectations on the company’s future outlook. The company justified this operation by saying that it will significantly lower capital expenditures and thereby increase return on assets. However, investors have perceived this change as a symptom that the company has become more pessimistic on future demand projections for its vehicles and realised that constructing a plant with higher production targets wouldn’t have paid off both in the short and long-term.
Will NIO recover?
In the short-term, the company’s financials might not at all be reassuring potential investors. In 2018, the company reported about $1.4B of losses backed by a mere 720M of revenues. Furthermore, the company reported negative $1.15 million of operating cash flows in 2018. Yet, we have to consider that NIO in a cash burning industry like the automobiles sector, that requires heavy investments in research and development to remain competitive. Being a new firm, it will take time for the company to develop and expand its business and actually start cashing in the heavy amount of R&D expenses it has to undertake. In this sense, Tesla can be a good benchmark for NIOs’ future performance, as it witnessed similar shocks in the evolution from a startup to a world automobile producer and eventually managed to improve its financial position. Given the large decline in stock price in the last months, NIO could represent a “buy” opportunity for investors who still believe in the long-term potential of the company.
Although there has been pessimism around NIO in the past months due to declining deliveries, we don’ t have to forget that it operates in a constantly growing market and that the firm has many features that distinguish it from its competitors. Indeed, NIO has one of the highest user satisfactions in the industry due to is strong innovative practices. Firstly, NIO is the only company with battery swap technology that, through NIO battery swap centres, allows customers to receive a fully swapped battery within 5 minutes. Furthermore, the company has a peculiar distribution model through which it conducts vehicle sales directly to users through its mobile application and the so-called NIO Houses. The appreciation for these innovative practices is testified by the around 800,000 users on its mobile application app. With the beginning of deliveries of the ES6 in June 2019, outlook on NIO might improve.cHowever, it is worth noticing that NIO might suffer rising competition from Tesla, which is its main competitor in the Chinese premium EV market. Recently, NIO vehicles have had a price advantage with respect to Tesla as Tesla had to bear import costs and ocean transport when selling vehicles in China. According to Tesla, this has made it operate at a 55-60% cost disadvantage. However, this might not the be case anymore as Elon Musk has announced the construction of a Tesla factory in Shanghai, which will begin partial production in the second half of the year and will each full production by 2020. This will significantly reduce Tesla’s costs and might therefore adversely affect NIO’s revenues.
Francesco Marino
The last important factor that caused market pessimism around NIO was the company’s decision to terminate the plan of building a manufacturing plant in Shanghai. On the contrary, NIO has entered into an agreement with JAC to jointly manufacture cars in JAC’s plant in Hebei. The plant with JAC is expected to remain in force for the next 2-3 years and is expected, after upgrades, to have an annual capacity of 150,000 units. In the long-run, NIO announced it will still focus on joint manufacturing and could potentially enter into agreements with other manufacturers as well. This decision has caused investors to submit a class action, alleging the company misled investors on its intentions regarding the Shanghai plant at the time of its IPO. According to them, the company’s SEC statements almost guaranteed that the plant was going to be constructed. The fact it didn’t is perceived by investors as a fraud since it significantly changes their expectations on the company’s future outlook. The company justified this operation by saying that it will significantly lower capital expenditures and thereby increase return on assets. However, investors have perceived this change as a symptom that the company has become more pessimistic on future demand projections for its vehicles and realised that constructing a plant with higher production targets wouldn’t have paid off both in the short and long-term.
Will NIO recover?
In the short-term, the company’s financials might not at all be reassuring potential investors. In 2018, the company reported about $1.4B of losses backed by a mere 720M of revenues. Furthermore, the company reported negative $1.15 million of operating cash flows in 2018. Yet, we have to consider that NIO in a cash burning industry like the automobiles sector, that requires heavy investments in research and development to remain competitive. Being a new firm, it will take time for the company to develop and expand its business and actually start cashing in the heavy amount of R&D expenses it has to undertake. In this sense, Tesla can be a good benchmark for NIOs’ future performance, as it witnessed similar shocks in the evolution from a startup to a world automobile producer and eventually managed to improve its financial position. Given the large decline in stock price in the last months, NIO could represent a “buy” opportunity for investors who still believe in the long-term potential of the company.
Although there has been pessimism around NIO in the past months due to declining deliveries, we don’ t have to forget that it operates in a constantly growing market and that the firm has many features that distinguish it from its competitors. Indeed, NIO has one of the highest user satisfactions in the industry due to is strong innovative practices. Firstly, NIO is the only company with battery swap technology that, through NIO battery swap centres, allows customers to receive a fully swapped battery within 5 minutes. Furthermore, the company has a peculiar distribution model through which it conducts vehicle sales directly to users through its mobile application and the so-called NIO Houses. The appreciation for these innovative practices is testified by the around 800,000 users on its mobile application app. With the beginning of deliveries of the ES6 in June 2019, outlook on NIO might improve.cHowever, it is worth noticing that NIO might suffer rising competition from Tesla, which is its main competitor in the Chinese premium EV market. Recently, NIO vehicles have had a price advantage with respect to Tesla as Tesla had to bear import costs and ocean transport when selling vehicles in China. According to Tesla, this has made it operate at a 55-60% cost disadvantage. However, this might not the be case anymore as Elon Musk has announced the construction of a Tesla factory in Shanghai, which will begin partial production in the second half of the year and will each full production by 2020. This will significantly reduce Tesla’s costs and might therefore adversely affect NIO’s revenues.
Francesco Marino